dtxrd¶
x-ray diffraction calculator (dynamical theory of x-ray diffraction)
| author: | Stanislav Stoupin |
|---|---|
| email: | <sstoupin@gmail.com> |
SYNOPSIS¶
dtxrd [options] crystal h k l eta phi T d ["a" | "e"] [theta | Ex]
DESCRIPTION¶
Calculates parameters of a given crystal reflection for a monochromatic incident wave using dynamical theory of x-ray diffraction for perfect crystals in the 2-beam approximation
For a brief summary run:
dtxrd -h
INPUT PARAMETERS¶
| crystal: | available crystal models: C (diamond), Si (silicon), Ge (germanium), GaN (wurtzite), SiC-4H, SiC-6H, SiO2 (quartz), Al2O3 (sapphire) |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| h k l: | Miller indicies of a chosen reflection |
||||||
| eta: | asymmetry angle (\(\eta\) [degrees]) |
||||||
| phi: | azimuthal angle of incidence (\(\phi\) [degrees]) |
||||||
| T: | crystal temperature [K] |
||||||
| d: | crystal thickness [mm] |
||||||
| flag: |
|
||||||
| theta: | glancing angle of incidence, theta (\(\theta\)) |
||||||
| Ex: | photon energy, Ex (\(E_{\mathrm X}\)) |
OPTIONS¶
| -v, --version: | |
|---|---|
| show program version | |
| -h, --help: | |
| show summary of options. | |
| -o FILENAME, --output FILENAME: | |
| write results to file (default to stdout) | |
| -w FILENAME, --write FILENAME: | |
| write data to file (default: no action) | |
| -p, --pi: | \(\pi\) polarization for the incident wave (default: \(\sigma\) polarization) |
| -c CONST, --conv CONST: | |
| convolve the reflectivity curve with a virtual instrument resolution function with FWHM = CONST [urad], plot the result and and report the resulting width of the convoluted curve | |
| -s CONST, --syield CONST: | |
| calculate shape of the secondary yield curve (e.g., photoelectrons) with escape depth CONST [Angstrom] | |
| -z STRING, --zblock STRING: | |
| calculate reflectivity/transmissivity curves for a mosaic crystal (uncorrelated block model) with STRING = 't s', where t is the block thickness [um] and s is the standard deviation of misorientation [urad] (assuming Gaussian distribution) | |
| -n CONST, --nsteps CONST: | |
| CONST - number of points in the angular/energy interval (default: 1000) | |
OUTPUT PARAMETERS¶
Basic parameters of the chosen h k l reflection:
| d[A]: | \(d\) [Angstrom] interplanar distance (d-spacing) of the chosen h k l reflection |
|---|---|
| Eb[keV]: | \(E_B = \frac{hc}{2d}\) [keV] Bragg energy |
| thr[deg]: | \(\theta_R\) [degrees] incident glancing angle for the exact backscattering (a wave with photon energy \(E_R\) incident at this angle is reflected exactly backwards) |
| Er[keV]: | \(E_R\) [keV] photon energy for the exact backscattering |
| bh: | \(b_{H}\) asymmetry factor in the chosen scattering geometry for symmetric reflection \(\eta = 0\) and \(b_{H} = - 1\) |
Susceptibilities and refraction corrections:
| chi_{0}: | \(\chi_0\) susceptibility |
|---|---|
| chi_{h}: | \(\chi_{H}\) susceptibility |
| chi_{-h}: | \(\chi_{\bar{H}}\) susceptibility |
| wh(s): | \(\omega_{H}^s\) refraction correction for symmetric reflection |
| wh: | \(\omega_{H} = \omega_{H}^s \frac{b_{H}-1}{2b_{H}}\) refraction correction for the chosen reflectoin |
Central energy and angle:
| Ec[keV]: | \(E_c\) [keV] central energy of the chosen reflection |
|---|---|
| thc[deg]: | \(\theta_c\) [deg] central glancing angle of incidence of the chosen reflection |
Energy intrinsic (Darwin) widths (thick non-absorbing crystal) at fixed glancing angle of incidence \(\theta_c\):
| eps_s: | \(\varepsilon^s\) relative energy width of symmetric h k l reflection (same for entrance and exit) |
|---|---|
| eps: | \(\varepsilon\) relative entrance energy width of the chosen h k l reflection |
| eps_pr: | \(\varepsilon'\) relative exit energy width of the chosen h k l reflection |
| Delta_E_s[meV]: | \(\Delta E^s\) [meV] absolute energy width of symmetric h k l reflection (same for entrance and exit) |
| Delta_E[meV]: | \(\Delta E\) [meV] absolute entrance energy width of the chosen h k l reflection |
| DeltaE_pr[meV]: | \(\Delta E'\) [meV] absolute exit energy width of symmetric reflection |
Angular intrinsic (Darwin) widths (thick non-absorbing crystal) at fixed photon energy \(E_c\):
| dth_s[urad]: | \(\Delta \theta^s\) [microradian] angular width of the symmetric h k l reflection (same for entrance and exit) |
|---|---|
| dth[urad]: | \(\Delta \theta\) [microradian] angular entrance width of the chosen h k l reflection |
| dth_pr[urad]: | \(\Delta \theta'\) [microradian] angular exit width of the chosen h k l reflection |
Additional characteristics of the chosen h k l reflection:
| dE/dth[meV/urad]: | |
|---|---|
| \(\frac{dE}{d\theta}\) [meV/microradian] tangent of the Bragg's Law | |
| Dr[urad/meV]: | \(D_r\) [microradian/meV] intrinsic angular dispersion rate of the chosen h k l reflection |
| de[um]: | \(d_e\) [micrometer] extinction length of the chosen h k l reflection |
Reflectivity and Transmissivity:
| Rc[%]: | \(R_c\) [%] reflectivity at center |
|---|---|
| Tc[%]: | \(T_c\) [%] transmissivity at center |
EXAMPLES¶
A rocking curve of the symmetric Si 111 reflection (Bragg case, 1-mm-thick crystal at 300 K)
dtxrd Si 1 1 1 0 0 300 1 e 8
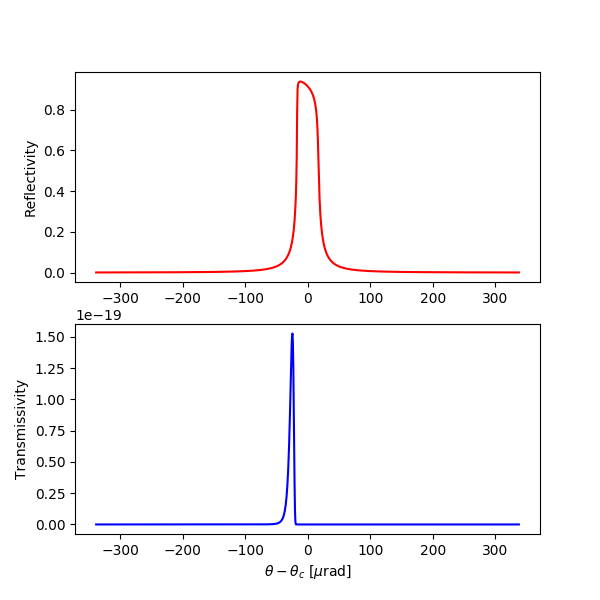
A rocking curve of the symmetric diamond 220 reflection (Laue case, 0.1-mm-thick crystal plate at 300 K)
dtxrd C 2 2 0 90 0 300 0.1 e 12
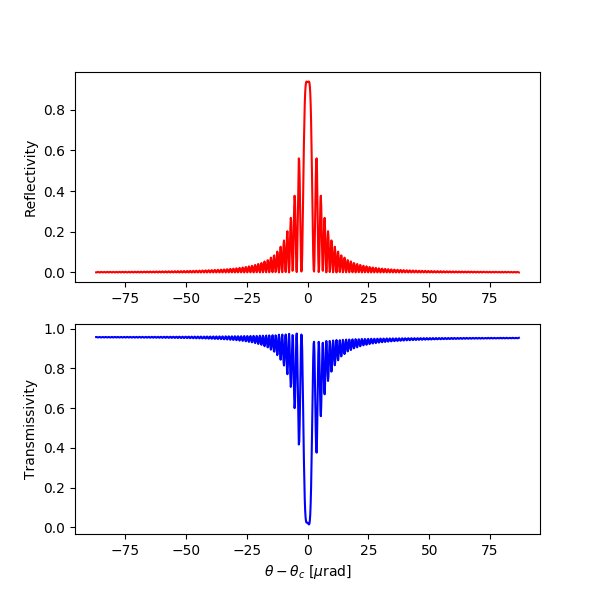
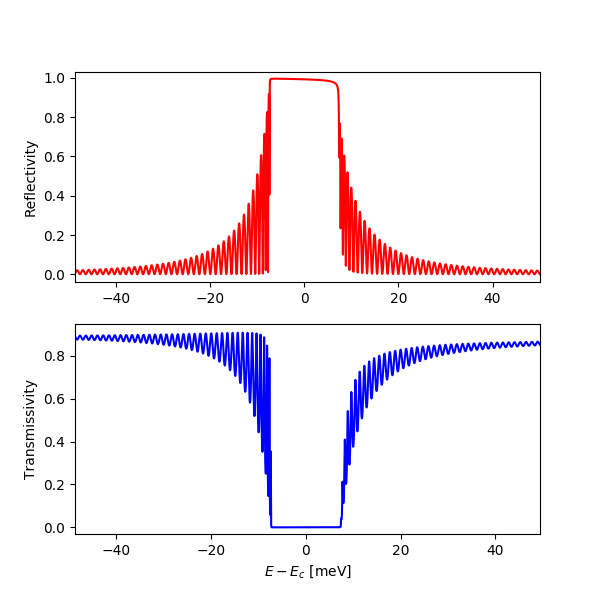
Reflectivity curve of the diamond 008 reflection in exact backscattering (0.5-mm-thick crystal plate at 300 K). Accurate sampling of the thickness oscillations is achieved using 10000 points.
dtxrd -n 10000 C 0 0 8 0 0 300 0.5 a 90
Rocking curve of the diamond 220 reflection (0.5-mm-thick crystal plate at 300 K at 20 keV). Reflectivity/transmissivity of a perfect crystal compared with those of the mosaic crystal with 10 um block size having misorientation of 20 microradian r.m.s. (uncorrelated block model)
dtxrd -n 10000 -z '10 20' C 2 2 0 90 0 300 0.5 e 20
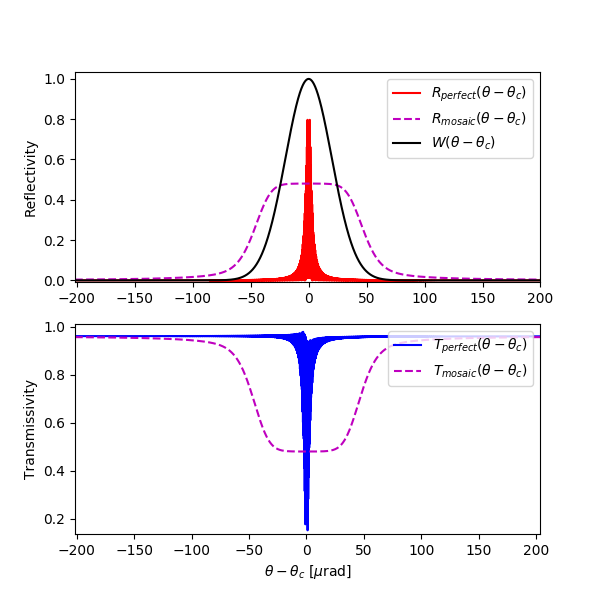
Note: reflectivity for a mosaic crystal in backscattering has not been implemented yet